- The Moneycessity Newsletter
- Posts
- 5 MISTAKES Exposing Your Bitcoin ID
5 MISTAKES Exposing Your Bitcoin ID
Can Bitcoin be traced, and most importantly how can you keep Bitcoin anonymous and protect your Bitcoin? I will explain 5 of the best ways to keep your Bitcoin secure. Bitcoin traceability is affected by the tools you use, like a VPN or a TOR, storing your private key on a paper wallet or custodial wallet, whether you cash out at an exchange or Bitcoin ATM, make transactions on a P2P marketplace, or use Bitcoin tumbler.
Bitcoin is only untraceable until you make a mistake.
Your interactions with Bitcoin can be divided into 5 steps. A mistake at any one step could mean your privacy is destroyed for that Bitcoin account.
You can think of each step as a link in a chain. One weak link and the whole chain is weak.
On the go? Watch my video HERE.
FIRST LINK
The first link I want to talk about is receiving Bitcoin.
You can think of your Bitcoin address as a see-through P.O. box. When Bitcoin hits your account or your Bitcoin address, anybody can see what’s in the P.O. box and anybody can see the number on the P.O. box. But nobody necessarily has to know who owns the P. O. box.
In this case, the number on the P.O. box is the public key. A public key is a 34-character long string that consists of numbers and letters that define your specific Bitcoin address.
And then the key that allows you to open that P.O. box is known as your private key which is a 64-character long string of numbers and letters.
What’s different though is when you tell somebody your public key or your P.O. box, they have access to everything that has come in and out of that P.O. box and who it was exchanged with for the history of that P.O. box.
This is because of the blockchain.

Bitcoin address, public key, and private key illustration by author
The Bitcoin network uses the blockchain for security. The blockchain is like a distributed public ledger that everybody has access to that records every transaction of Bitcoin in the history of Bitcoin.
The Bitcoin network is set up to only allow changes to the blockchain if the majority of the people on the Bitcoin network agree to the change.
This makes it hard to steal or add money erroneously with everybody watching and is great for security, but now you know what you’re up against if you want to remain private on the Bitcoin network.
For instance, if you have a business and you want to take payments for your business in Bitcoin, you can’t have your public key tied to your business that’s in your name. Otherwise, it’s a really easy leap. Anybody can see that this public key is tied to your business, which is tied to your name. So, you’re going to have to take payments anonymously.
Essentially, this boils down to keeping your identity as far away as possible from your public key. Once these two things are linked, it’s over.
SECOND LINK
The second link in your chain is spending Bitcoin.
Now there are a lot of vendors out there that will accept Bitcoin. But you’re gonna have to be very choosy if a vendor requires a physical address, phone number, or email address. These are all things that can be tied to your identity.
This means that you can make transactions with a vendor that doesn’t require any kind of identifiable information or a party that will use a Bitcoin tumbler.
The way a Bitcoin tumbler works is it’s a stepping stone between you and whoever you’re exchanging Bitcoin with.

Bitcoin Tumbler Illustration
For example, I and 100 others will send Bitcoin to the tumbler, and then the tumbler will distribute it to whoever we want to pay. Now from the outside, it’s hard to tell who exactly I was paying, because my Bitcoin and 100 other Bitcoins all went in, and then it got distributed to a whole bunch of people.
So, these can kind of work, but they also have their downsides.
For instance, if Bitcoin has been through a tumbler, then that is in the blockchain, and some vendors or exchanges will no longer accept that Bitcoin because it’ll be considered dirty money.
THIRD LINK
The third link in the chain is how you hold your Bitcoin.

Bitcoin Wallet Illustration
Bitcoin wallet is a little bit of a misnomer. Your Bitcoin wallet is more like a keychain. This is really where you store your private key. All of the Bitcoin is held in a Bitcoin address on the Bitcoin network. But how you access that Bitcoin is by using your private key.
When it comes to storing your private key, there is a trade-off between security and convenience.
The most secure wallet is a paper wallet.
This is exactly what it sounds like. You write down your private key on a piece of paper and then you put that piece of paper in a safe or something. Now this is very inconvenient because the private key is 64 characters long with random numbers and letters.
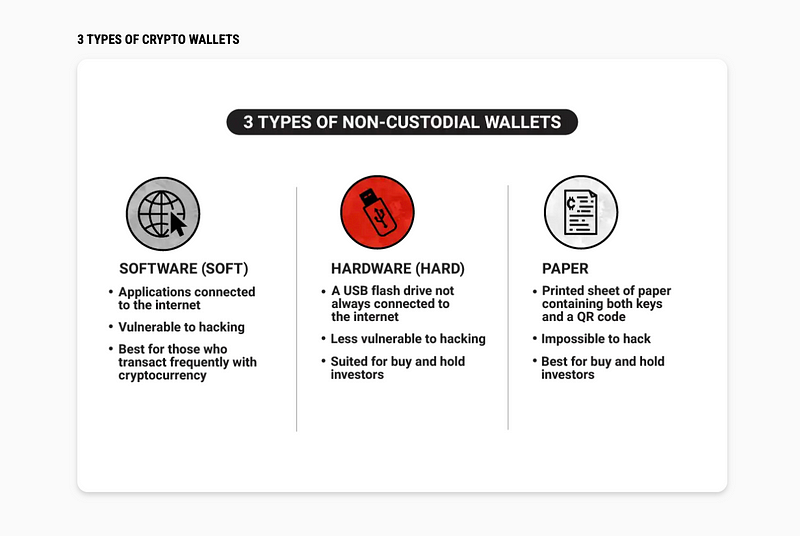
Types of Crypto Wallet
Whenever you want to make a transaction, it is super tedious to have to enter that key every single time. If you think modern password requirements are annoying now, imagine if you had to do a 64-character password of random numbers and letters every time you logged in to your account.
A paper wallet is incredibly secure against cyber attacks. It can’t leak, but it is not very secure against the washing machine if you leave that piece of paper in your pants pocket.
On the other end of the spectrum, the most convenient way to store your private key is through a custodial wallet like Coinbase. Coinbase will hold your private key for you. So they technically own your account, and then you log into Coinbase with your username and password.
If you forget your private key or you forget your password, Coinbase has customer service that can help you recover your account.
The downside of using a custodial wallet like Coinbase is:
They have your private key. So weirdly, they kind of own your Bitcoin.
They have your identity. So now you’re relying on Coinbase to be secure with your information. If they leak or if they get hacked, you could lose all of the privacy that you worked so hard to achieve.
The best answer is probably somewhere in the middle, perhaps an anonymous, non-custodial wallet.
This gives you more responsibility, but it also gives you a lot more privacy. You can store your private key on a hard drive. That way, you’re not vulnerable to a leak or a hack, and you still don’t have to type in your key every time, you just have to plug in your hard drive.
FOURTH LINK
The fourth link of the chain is cashing out your Bitcoin. Once again, there is a major trade-off between convenience and privacy.
You can forget about going to an exchange.
I know I mentioned earlier that if your Bitcoin has been through a Bitcoin tumbler, then an exchange won’t accept it. Well, if you’re trying to maintain your privacy, you don’t want to go to an exchange anyway.
They will require your identification because of government regulations concerning money laundering. This is a requirement for all exchanges, so you’re going to have to stay away.
One decent option is a Bitcoin ATM. Some of these will require identification. Others will not.
If you can find one that does not, the only downside here is that they will have a daily maximum, maybe $100 or $200. So you’re going to have to hit a whole bunch of ATMs in a day for several days to cash out a meaningful amount of Bitcoin.
Additionally, if you’re trying to be super private, you’ve got to be walking around. There might be cameras. You’re going to have to wear a trench coat, a hat, dark sunglasses, and a fake mustache. So that could be an upside, depending on if you like that, if you’re into that sort of thing.
Another potential option is through peer-to-peer transactions. There are two types.
In-person peer-to-peer transactions: You can join Facebook groups to connect with people in your area who are looking to exchange Bitcoin for cash. This is a little bit risky because you could be robbed, so find a place to do this in public.
Online peer-to-peer transactions: Using an online marketplace is going to be way more convenient and more safe. However, they have to send your cash somewhere. Once you give somebody an account that they can send money to, that can be tied to your identity, there’s always the chance it could be linked in the future. Now, since you’re dealing with just an individual, and not a company or a bank that has to keep records, your chances of your identity being linked are a lot less.
Now, even if you do all the things so far perfectly, you are still vulnerable if you have a weak fifth link.
FIFTH LINK
The fifth way that your identity can be commonly linked to your transaction history is through your IP address.
Even if you do all the previous steps perfectly, once your public key is tied to your IP address, it can be tied to your physical address, and then to your identity.
Bitcoin does not have any built-in encryption for broadcasting transactions through its network. Your internet service provider can intercept these broadcasts and determine which IP address is associated with which Bitcoin address.
If you do not want your internet service provider to have access to your entire Bitcoin transaction history, then you can use a VPN or a TOR. These are not the same thing, but they both serve as a block between your internet service provider and whatever websites you are visiting.
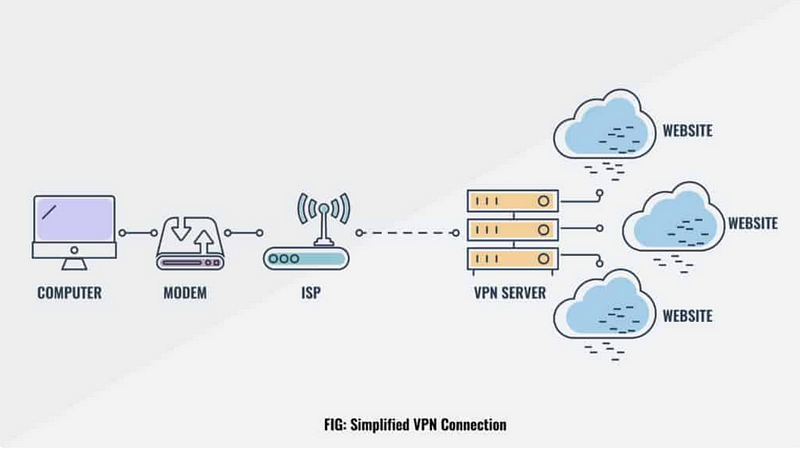
VPN Illustration
If you use a VPN or a TOR, it makes it almost impossible for your internet service provider to link your transaction to your Bitcoin address.

TOR Illustration
Keep in mind, maintaining your privacy is great but it will not shield you from losing a lot of money with Bitcoin.
Bitcoin is incredibly volatile and its value swings by tens of thousands of dollars in a pretty short period of time. So, check out this deep dive where I show you where Bitcoin’s value comes from. That way you’ll be able to make more informed investing decisions.
Until next time.rab

Reply